Mathematics of Blackjack

Variance
Variance a term we all hear a lot but may not fully understand what it is. In a gambler’s world, if they hear this they will just say “hey that’s just a fancy word for luck”. By definition it is simply the difference in the expected advantage and the actual results produced. For example, let’s say you are playing a decent counting game and your hourly EV is $25 an hour. You play for a total of 100 hours and your expectation for those 100 hours is $2, 500. You take a look at your logs and realized you are only $2000 ahead. This shows you are $500 below expectation which is the VARIANCE of what you would expect to win, on the flip side you could always be $500 ahead of your EV.
*You were using a bet spread worth $25/hr, but after 4 hours, you were up or down $1500. You just experienced Variance, my friend. The good news (if you’re a winning player) is that the more hours you play, the closer you get to variance balancing out, and all you are left with is the “long run”.
Standard Deviation (SD)
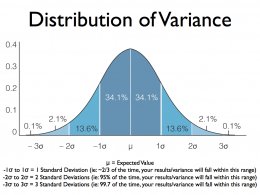 By Definition a standard deviation refers to how far or how often an outcome will deviate from the average. Standard deviation and variance go hand in hand (SD is actually the square root of variance). At this point you are probably asking yourself “how do these things affect me as a player?” There is not one answer for this, but a multiple set of answers. Figuring what variance you have in a game and what the SD is for any particular game at any stakes can help you assess if you are playing a winning game or how much bankroll you need to bring to a session.
By Definition a standard deviation refers to how far or how often an outcome will deviate from the average. Standard deviation and variance go hand in hand (SD is actually the square root of variance). At this point you are probably asking yourself “how do these things affect me as a player?” There is not one answer for this, but a multiple set of answers. Figuring what variance you have in a game and what the SD is for any particular game at any stakes can help you assess if you are playing a winning game or how much bankroll you need to bring to a session.
*Standard Deviation helps prepare you for what to expect, in terms of variance. If you are consistently experiencing results beyond 2 SD, you’re either one lucky/unlucky SOB, or something doesn’t add up!
N-Zero (N0)
N0 is something not looked at very often especially among new players. N Zero is the number of hands theoretically required before hitting a goal of being ahead by one standard deviation (4*N0 gives you the hours to overcome 2 SD). To get the most accurate evaluation of N0 one must play by the same set of rules and the same betting/playing strategies. Going back to our original example of $25 EV per hour, we would find our N0 by the following equation N0= Variance/EV^2.
*Want to overcome variance (i.e. luck) and get to the “long run” quicker? Play games and use bet spreads that have a lower N0.
Certainty Equivalence (CE)
This is also known as risk-adjusted return. This is the product of taking the expected win rate and adjusting it based on the level of risk in proportion to the current bankroll and level of risk tolerance. This will show you if the game is “worth playing” compared to your bank size. So you may have a $100 in EV but you CE may only indicate that the game is only worth $50 since your bankroll is so small. You can even go so far as CE going into negative territory which indicates you are severely over betting your bankroll.
Donald "Don" Schlesinger is a gaming mathematician, author, lecturer, and player who specializes in the casino game of blackjack. His work in the field has spanned almost three decades. He is the author of the book Blackjack Attack - Playing the Pros' Way, currently in its third edition, which is considered one of the most sophisticated...


|
Blackjack Strategy: Winning at Blackjack:Tips and Strategies for Winning and Dominating at the Casino (Blackjack, Counting Cards, Blackjack Winning, Good at Blackjack, Black Jack, Card Counting) eBooks |